Elastic Network Inferfaces are logical components in your AWS Virtual Private Cloud which present Virtual Network Cards. ENI can be created independently of EC2 Instances and can be assigned at any time on the fly and moved from one instance to another. Each ENI has the options of:
1. One primary private IPv4 address and can have one or more secondary private IPv4 addresses
2. One Elastic IP address per private IPv4.
3. One Public IPv4 address
4. One or more security groups
5. A MAC address
6. ENI are bound to one availability zone.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1. Logon to AWS as an IAM user at URL: https://signin.aws.amazon.com/
2. From the Home Console type EC2 in the search bar, select the star next to EC2, and select EC2

3. On the let hand menu bar select Network Interfaces.

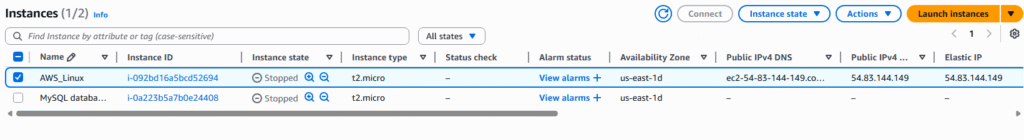
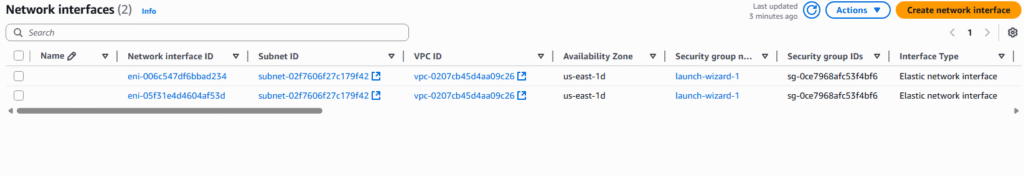
4. The page will display all currently existing ENI, we currently have created two EC2 Instances and AWS created two ENI for them by default. Select Create network interface.
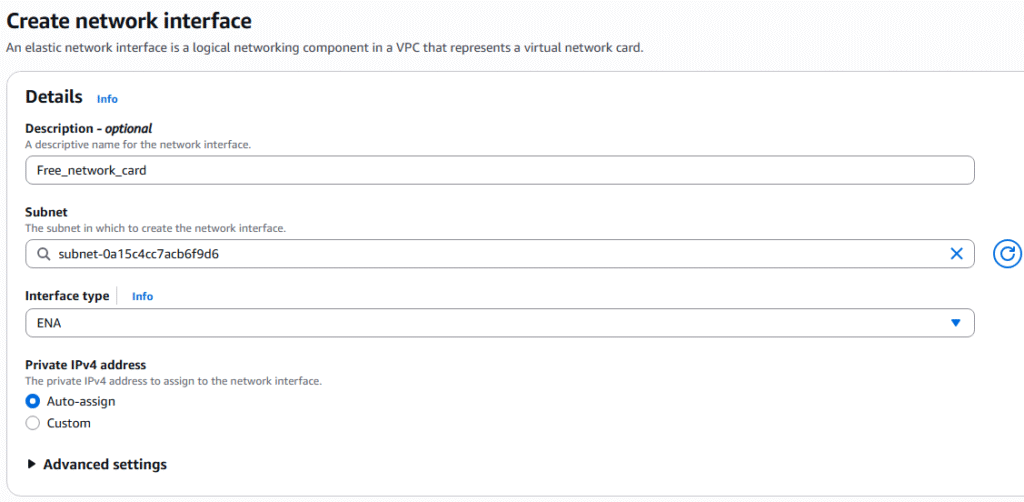
5. Under details, enter the description of your network card, the subnet, Interface type, and Auto-assign of IP address.
6. In the security groups section, select an existing group and enter a Tag if desired. Click the Crete network interface to proceed.
7. The creation will be confirmed on the next page.
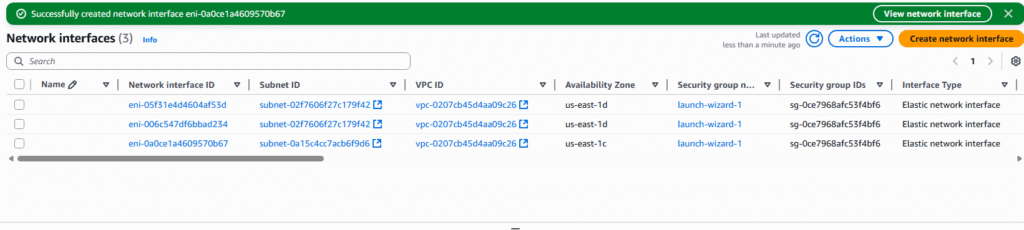
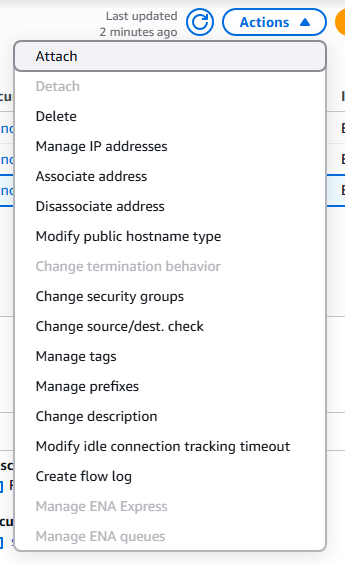
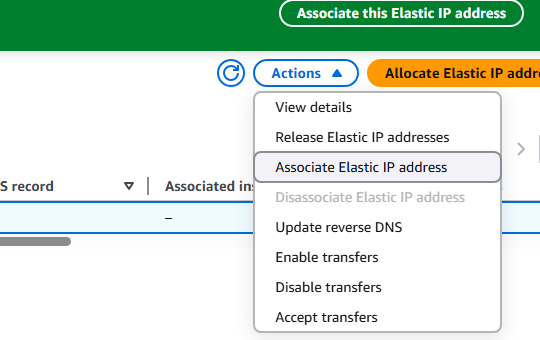
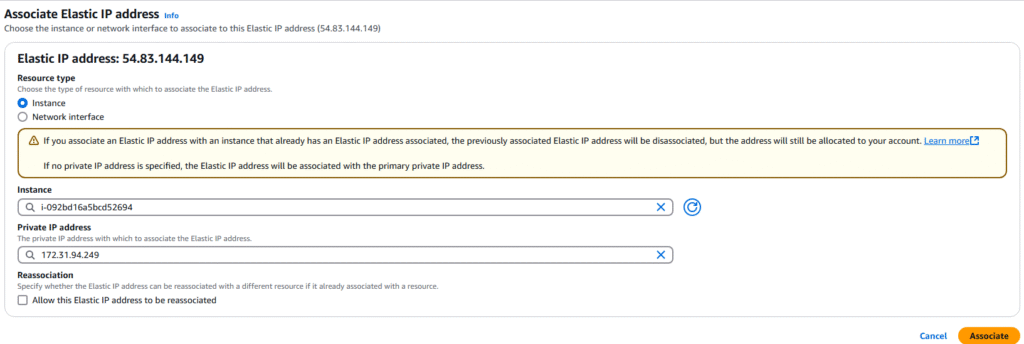
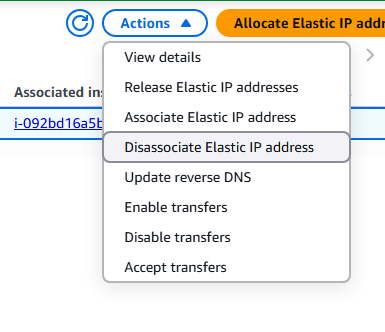
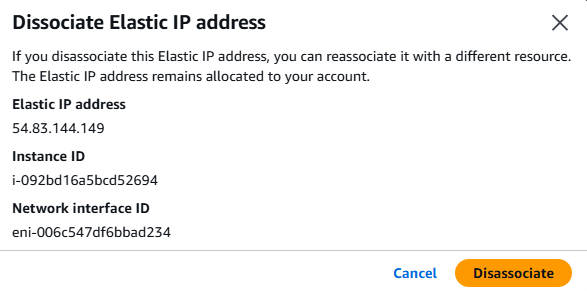
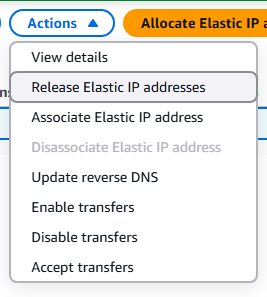
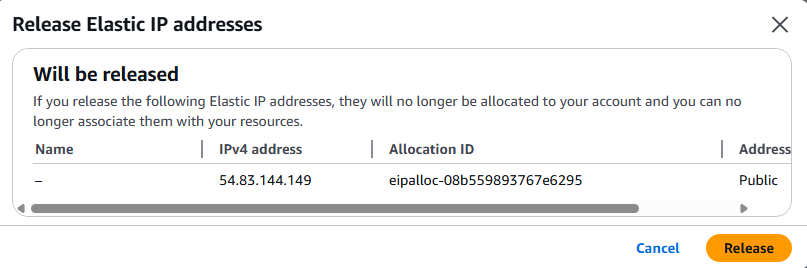
8. You can modify, associate, or delete the ENI by clicking on the ENI of choice and select Actions.