AWS Amazon Aurora is a database engine developed by Amazon and offered as a service by AWS. Aurora has the following characteristics:
1. Aurora is a proprietary technology of AWS and is not open source.
2. Fully compatible with Postgres and MySQL, all drivers for these database engines will work with Aurora.
3. Aurora is “AWS cloud optimized” and it is claimed that you can achievet 5x faster than MySQL and 3x faster than Postgres.
4. Aurora automatically grows in 10GB chunks up to 128TB
5. Aurora can have 15 replicas and replication is after than other RDSs
6. Failover in Aurora is instantaneous and is High Availability native.
7. Aurora cost more than other RDS by 20%, but it is more efficient.
8. Automatic fail-over
9. Backup and Recovery
10. Isolation and security
11. Industry compliance
12. Push-button scaling
13. Automatic patching with zero downtime
14. Advanced Monitoring
15. Routine Maintenance.
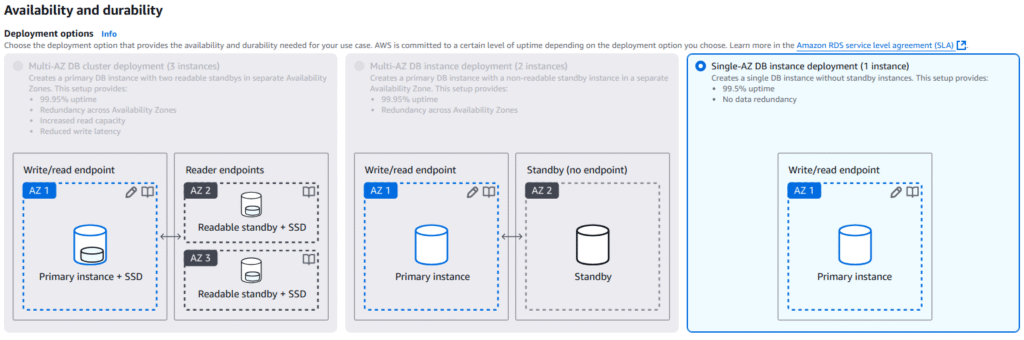
Aurora High Availability and Read Scaling
1. 6 copies of you data across 3 AZ
a. 4 copies out of 6 needed for writes.
b. 3 copies out of 6 needed for reads.
c. Provides self healing by way of peer to peer replication.
d. Storage is striped across 100s of volumns.
2. One Aurora Instance takes the writes and is the master copy.
3. If Master fails the failover is less than 30 seconds.
4. Master + 15 Read Replicas and any of the Read Replicas can be promoted to Master.
5. Read Replicas support Cross Region Replication
Aurora DB Cluster
1. Applications are given a Writer Endpoint which points to the Instance which currently is the Master.
a. This Writer Endpoint will redirect traffic to new Master if it changes.
2. Application are given a Reader Endpoint which connects to read replica copies through load balancing
a. This Reader Endpoint will remove instance that is promoted to Master