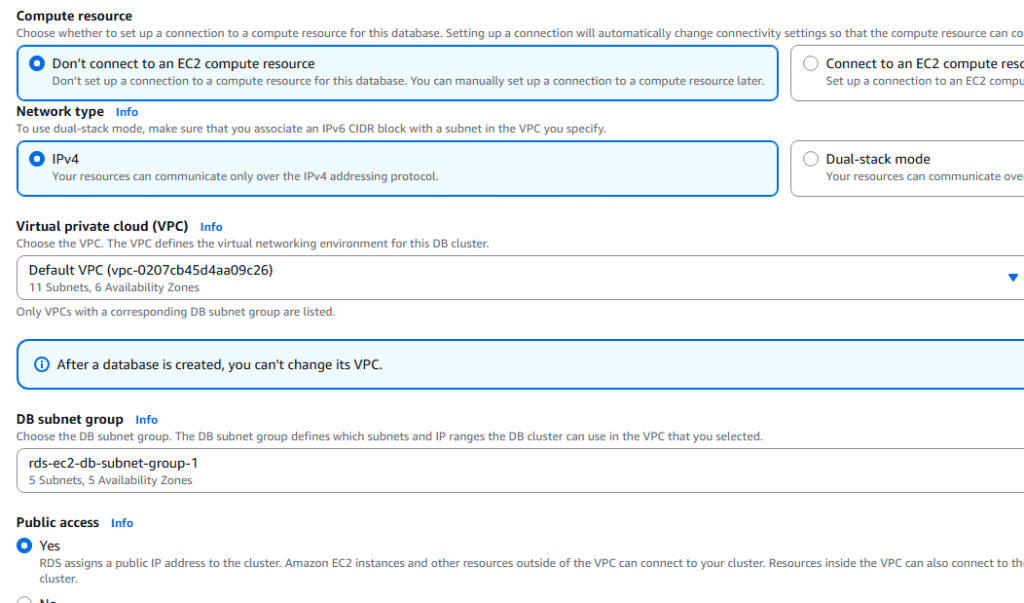
AWS Certificate topics cover a lot of advance topics on Aurora RDS. This article attempts to cover all questions which maybe asked about Aurora.
Aurora Replica Auto Scaling
- Automatically increasing the number of read replica database based on increased CPU usage.
- Reader endpoint automatically increased to accommodate new read replica databases.
- Reader endpoint load balances over all read replica databases.
Aurora Custom Endpoints
- You create some read replica database on larger EC2 instances for RDS.
- Create Custom endpoint to allocate resources to larger EC2 instances for RDS.
- Use case some process require more compute power from Read Replica IE Analytics.
- You no longer use the read endpoint but setup different custom endpoints for different types of processing.
Aurora Serverless
- Automated database instantiate and auto scaling based on usage
- Good fro infrequent, intermittent or unpredictable workloads.
- No capacity planning required.
- Pay per second of use and can be more cost-effective.
- Client goes through Proxy Fleet which determines the number of Aurora databases needed for the workload.
Global Aurora
- Aurora Cross Region Read Replica
- Useful for disaster recovery.
- Simple to put in place.
- Aurora Global Databases (recommended)
- 1 Primary Region (read/write)
- Up to 5 secondary (read-only) regions, replication lag is less than 1 second.
- Up to 16 Read Replicas per secondary region
- Helps for decreasing latency to clients.
- Promoting another region (for disaster recovery) has an RTO of less than 1 minute.
- Typical cross-region replication takes less than 1 second.
Aurora Machine Learning
- Enables you to add ML-based predictions to your applications via SQL
- Simple, optimized and secure integration between Aurora and AWS ML services
- Supported services
- Amazon SageMaker (use with any ML model)
- Amazon Comprehend (for sentiment analysis)
- You don’t have to have ML experience
- Use Cases: fraud detection, ads targeting, sentiment analysis, product recommendations
Babelfish for Aurora PostgreSQL
- Allows Aurora PostgreSQL to understand commands targeted for MS SQL Server (T-SQL)
- Therefore Microsoft SQL Server based applications can work on Aurora PostgreSQL
- Requires no to little code changes (using the same MS SQL Server client drivers)
- Same applications can be used after a migration of your database (using AWS SCT and DMS)